Viscosity dominated KGD hydraulic fracture
Description of the case
The KGD problem addresses a single plane strain fracture growing in an infinite elastic domain. Basic assumptions and characteristic shape for this example is similar to those of another case (Viscosity dominated KGD hydraulic fracture) except that the viscosity dominated regime is now considered. In this regime, more work is spent to move the fracturing fluid than to split the intact rock. In this test, slickwater with a constant viscosity of 1 cp is chosen as fracturing fluid, whose compressibility is neglected. To make the case identical to the viscosity dominated asymptotic solution, an ultra-low rock toughness is defined and fracture is assumed to be always propagating following fluid front.
Asymptotic solutions of the fracture length
, the net pressure
and the fracture aperture
at the injection point for the KGD fracture with a viscosity dominated regime are provided by (Adachi and Detournay, 2002):
where the plane modulus is defined by
and the term is given as:
Input file
The input xml files for this test case are located at:
inputFiles/hydraulicFracturing/kgdViscosityDominated_base.xml
and
inputFiles/hydraulicFracturing/kgdViscosityDominated_benchmark.xml
The corresponding integrated test with coarser mesh and smaller injection duration is also prepared:
inputFiles/hydraulicFracturing/kgdViscosityDominated_smoke.xml
Python scripts for post-processing and visualizing the simulation results are also prepared:
inputFiles/hydraulicFracturing/scripts/hydrofractureQueries.py
inputFiles/hydraulicFracturing/scripts/hydrofractureFigure.py
Fluid rheology and rock toughness are defined in the xml blocks below. Please note that setting an absolute zero value for the rock toughness could lead to instability issue. Therefore, a low value of is used in this example.
<SurfaceGenerator
name="SurfaceGen"
targetRegions="{ Domain }"
nodeBasedSIF="1"
initialRockToughness="1e4"
mpiCommOrder="1"/>
<CompressibleSinglePhaseFluid
name="water"
defaultDensity="1000"
defaultViscosity="1.0e-3"
referencePressure="0.0"
compressibility="5e-10"
referenceViscosity="1.0e-3"
viscosibility="0.0"/>
First, by running the query script
python ./hydrofractureQueries.py kgdViscosityDominated
the HDF5 output is postprocessed and temporal evolution of fracture characterisctics (fluid pressure and fracture width at fluid inlet and fracure half length) are saved into a txt file model-results.txt, which can be used for verification and visualization:
[[' time', ' pressure', ' aperture', ' length']]
2 1.075e+06 0.0001176 1.5
4 9.636e+05 0.0001645 2
6 8.372e+05 0.0001917 2.5
8 7.28e+05 0.000209 3
10 6.512e+05 0.000222 3.5
Note: GEOS python tools geosx_xml_tools should be installed to run the query script (See Python Tools Setup for details).
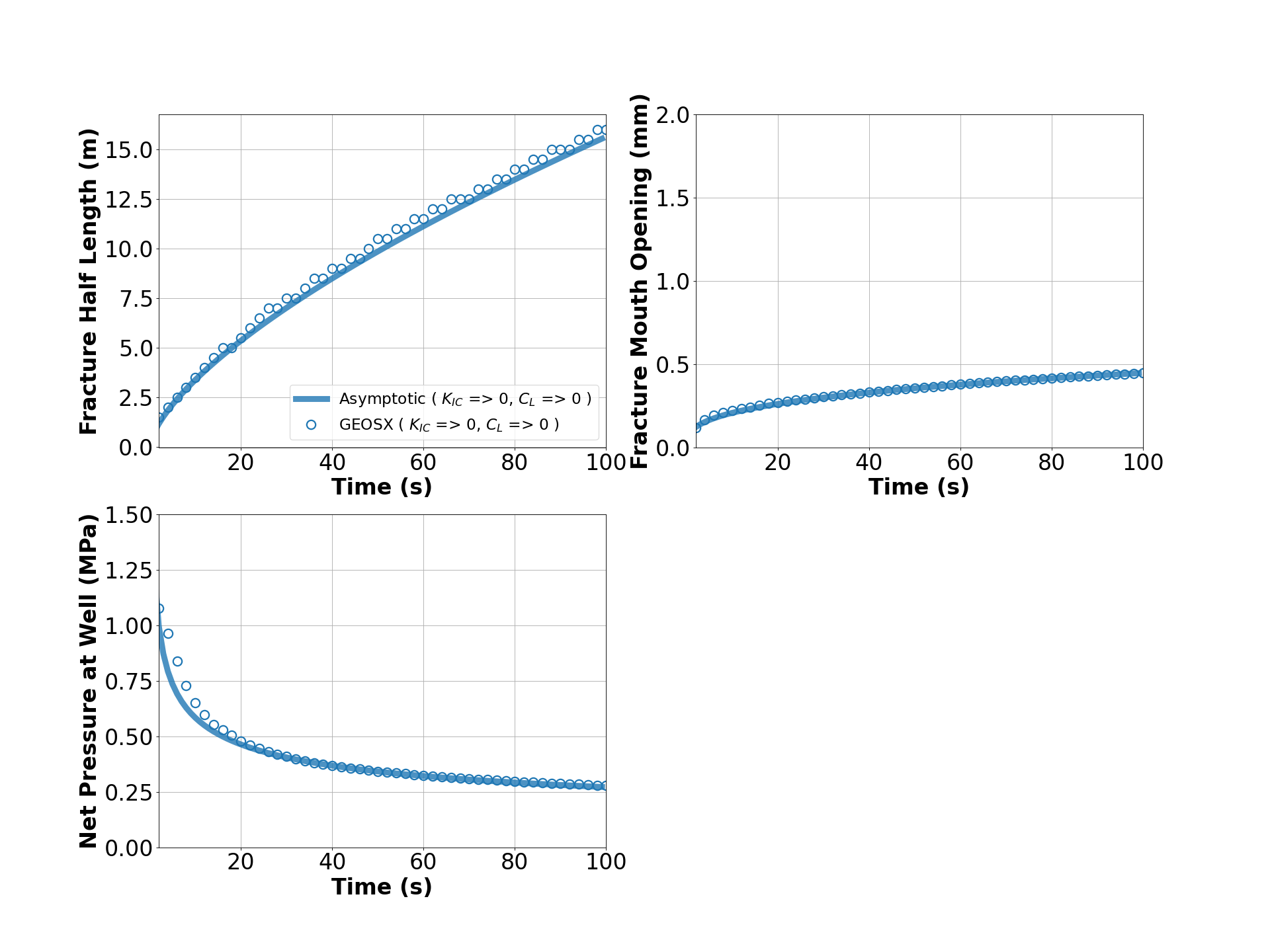
A good agreement between GEOS results and analytical solutions is shown in the comparison below, which is generated using the visualization script:
python ./kgdViscosityDominatedFigure.py
To go further
Feedback on this example
This concludes the viscosity dominated KGD example. For any feedback on this example, please submit a GitHub issue on the project’s GitHub page.